EXPERIMENT
RESPONSE OF FIRST ORDER
SYSTEMS (Step Change)
1.
INTRODUCTION
The thermometer is assumed to be at
steady state initially. This suggests that there is no change in temperature
with time, before time zero. At time zero the thermometer will be subjected to
some change in the surrounding temperature x(t).
By applying the unsteady-state energy balance
INPUT= OUTPUT + RATE OF ACCUMULATION
where,
A = surface area of bulb for heat
transfer, m2
h = film coefficient for heat transfer,
(kW/m2.◦C)
m = mass of mercury in bulb, kg
C = heat capacity of mercury, kJ/kg.◦C
t = time, sec
For steady state,
2. EXPERIMENTAL DESCRIPTION
 |
| Setup of first order system |
The
above apparatus used to study the response of first order system subjected to
step change. Thermowell is attached to the thermowell. The thermowell is filled
with oil providing an additional resistance. The Thermobath is attached to a
water pipeline for cooling the thermometer. A valve is attached at the bottom
of the thermobath to maintain the flowrate. A water head indicator is attached
to the thermobath to know the level of liquid in the bath.
3.
PROCEDURE
Start Up
• Fill
the heating bath with water.
• Switch
on the beeper and set the system’s beep interval to 3 sec.
• Ensure
that cyclic timer is set to 80 seconds ON time and 30 seconds OFF time.
• Switch
on the mains to heat water inside the heating bath to its boiling point.
• Switch
off the mains once the water reaches its boiling point.
• Insert
the thermometer in the heating bath instantaneously after noting its initial
temperature.
• Note
the thermometer reading at each beep interval till the temp. reaches steady
state.
Shut Down
• Switch
off the beeper and the system power supply.
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
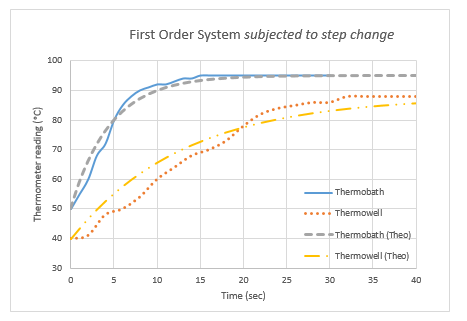 |
First order system subjected to
step change- 1st Set
|
The above figure shown the first order response
subjected to step change. Thermometer reading (C) is on the y-axis and Time
(second) is on the x-axis. The shape of both the curves are exponentially
increasing and attaining their ultimate values in 4-5 time constants as
mentioned in the literature. The maximum temperature of the thermowell that was
achieved was 88°C and that of the thermobath was 95°C. From above figure it
seem that the maximum temperature
attainable by a thermowell is lower than that for a thermobath because of an
additional resistance at its bulb to increase its time constant. Ultimate value
of temperature and the ultimate response time for thermowell are 78.44, 4.584
respectively. Ultimate value of temperature and the ultimate response time for
thermobath are 70.336, 13 respectively.
 |
| First order system subjected to step change- 2st Set |
The above figure shown the first order response
subjected to step change for set 2. Thermometer reading (C) is on the y-axis
and Time (second) is on the x-axis. The shape of both the curves are
exponentially increasing and attaining their ultimate values in 4-5 time
constants as mentioned in the literature. Ultimate value of temperature and the
ultimate response time for thermowell are 78.44, 4.49 respectively. Ultimate
value of temperature and the ultimate response time for thermobath are 70.704,
13 respectively.
6. CONCLUSIONS
The aim of this experiment was to
observe the response of a thermowell and thermobath subjected to a step change.
The maximum temperature of the thermowell that was achieved was 88°C and that
of the thermobath was 95°C. Temperature changes rapidly until it reached a
point where a slow change is observed. Ultimate value of temperature and the
ultimate response time for thermowell are 78.44, 4.584 respectively. Ultimate
value of temperature and the ultimate response time for thermobath are 70.336,
13 respectively. Temperature changes rapidly until it reached a point where a
slow change is observed.
7. REFERENCES
a) Coughanowr, D. E. & LeBlanc, S., 2009. Transient
Response of Simple Control System. In: Process
System Analysis and Control. New York : McGraw Hill, pp. 228-230.
b) Coughanowr, D. R. & LeBlanc, S. E., 2009. Introductory
Concepts. In: Process System
Analysis and Control. New York: McGraw Hills, pp. 2-3.


